Weightlifting vs. Bodyweight: The Ultimate Workout Showdown
In the vibrant arena of fitness, two titans stand at the forefront, each championing a distinct approach to building strength and sculpting the body. On one side, we have weightlifting, a traditional method steeped in time-honored techniques and the rhythmic clanking of metal weights. On the other, bodyweight training rises like a modern phoenix, harnessing the power of one’s own form to unlock potential without the need for specialized equipment. As fitness enthusiasts grapple with the age-old question of which method reigns supreme, we embark on a thorough exploration of these two modalities. From their unique benefits to their respective challenges, join us as we dive deep into the ultimate workout showdown, illuminating the strengths and weaknesses of weightlifting and bodyweight training. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or a curious beginner, this article aims to provide clarity in the pursuit of your fitness goals, helping you decide which path best aligns with your aspirations.
Exploring the Foundations of Strength: Weightlifting versus Bodyweight Training
When it comes to building strength,the two prominent training modalities—weightlifting and bodyweight training—offer unique benefits and challenges that can cater to different fitness goals. Weightlifting is often associated with progressive overload and targeted muscle progress, allowing individuals to lift heavier weights as they gain strength. This method primarily focuses on specific muscle groups, making it highly effective for those looking to increase muscle mass, enhance athletic performance, or achieve particular physique goals. The structured habitat of a gym provides access to various equipment, giving lifters the freedom to experiment with different techniques and intensities.
On the other hand, bodyweight training emphasizes functional strength and overall body control. Exercises like push-ups, pull-ups, and squats require no equipment and can be performed anywhere, making them incredibly versatile for daily life and travel. These movements engage multiple muscle groups concurrently, promoting a balanced strength development and improving core stability. Moreover, bodyweight training can be easily modified to match fitness levels—from beginner variations to advanced moves like muscle-ups and planches—thus fostering a progressive journey toward strength mastery.Both methods can coexist beautifully, offering a comprehensive approach to fitness when integrated thoughtfully.
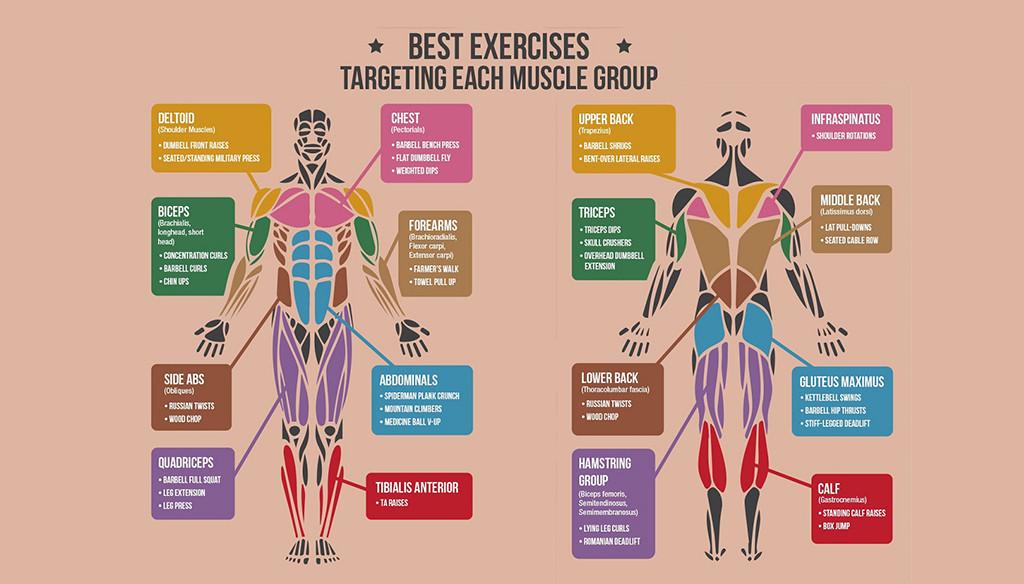
Target Muscles and Functional Fitness: An In-Depth Comparison
When it comes to comparing weightlifting and bodyweight exercises, the target muscles engaged play a crucial role in determining which workout method is more suitable for individual goals. Weightlifting predominantly focuses on isolating specific muscle groups, providing the ability to adjust the load for progressive overload. This structured approach often emphasizes the development of major muscle groups, including:
- Chest: Exercises like bench press and dumbbell flys
- Back: Pull-ups, rows, and deadlifts
- Legs: Squats and leg presses
Conversely, bodyweight training champions functional fitness by integrating multiple muscle groups into compound movements. This not only increases strength but also enhances coordination, balance, and flexibility. Key movements associated with this style include:
- Push-ups: Great for the chest,shoulders,and core stability
- Squats: Effective for legs while engaging the core
- Burpees: A full-body exercise that boosts cardiovascular fitness
| Workout Type | Target Focus | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Weightlifting | Isolation of muscle groups | Strength gains,hypertrophy |
| bodyweight | Functional movement patterns | Improved coordination,flexibility |

Injury Risks and Recovery: Understanding the Safety Profiles of Each Method
When comparing weightlifting and bodyweight training, understanding the injury profiles associated with each method is crucial for making informed decisions about your fitness journey. Weightlifting, while highly effective for building strength and muscle mass, comes with a set of risks primarily due to the heavier loads and complex movements involved. Common injuries include:
- Strains and Sprains: Overloading muscles or improper form can lead to tears, especially in the lower back and shoulders.
- Joint Issues: Heavy lifting places stress on joints, which may result in chronic pain or injuries over time.
- Overtraining: Not allowing adequate recovery can lead to fatigue-related injuries.
On the other hand,bodyweight training generally presents a safer alternative for individuals looking to minimize their injury risks. since this method relies on the individual’s body weight, the opportunity for excessive load is reduced, leading to a lower incidence of injury. however, it is not without its risks, which include:
- Insufficient Progression: Limited load can sometimes stunt muscle growth if not properly progressed.
- Form Fatigue: As repetitions increase, the quality of movement may decline, risking improper technique.
- Imbalance: Focusing solely on bodyweight exercises can neglect certain muscle groups.
| Method | Injury Risk | Common Injuries |
|---|---|---|
| Weightlifting | Higher | Strains, Joint Issues |
| Bodyweight | Lower | Form Fatigue, Imbalance |

Crafting the Perfect Regimen: Tailoring Your Workout for Optimal Results
When it comes to maximizing your fitness journey,determining the ideal workout for your goals is paramount. Weightlifting offers a methodical approach to building muscle mass, enhancing strength, and improving overall body composition. This style of training allows you to systematically increase resistance, providing your body with the stimulus it needs to adapt and grow. Key benefits include:
- Increased Muscle Hypertrophy: Progressive overload fosters muscle growth.
- Bone Density Improvement: Resistance training strengthens bones.
- Variety of Equipment: Access to various tools (e.g., dumbbells, bars, machines) allows for diverse routines.
Conversely, bodyweight exercises promote functional strength, flexibility, and agility, often making them more accessible to individuals regardless of fitness level.This approach capitalizes on the weight of your own body, focusing on movement patterns that engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Benefits to consider include:
- Cost-Effective: Requires no gym membership or equipment.
- Improved Core Stability: Many movements require core engagement, enhancing stability.
- Flexibility and Mobility: Promotes a greater range of motion and functional mobility.
| Aspect | Weightlifting | Bodyweight |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Needed | Yes | No |
| Skill Level Required | Intermediate to Advanced | Beginner Friendly |
| space Requirement | Gym or Home Gym | Any Space |
The Way Forward
As we conclude this exploration of the dynamic duo in the fitness world—weightlifting and bodyweight training—it becomes clear that the ultimate showdown is less about choosing one over the other and more about discovering what aligns with your personal fitness journey. Each approach offers unique benefits, from the muscle-sculpting potential of weights to the functional strength and flexibility gained through bodyweight exercises.Ultimately,the best workout is the one that resonates with you,fuels your passion,and aligns with your goals. Whether you prefer the controlled resistance of weights or the freedom of bodyweight movements, both paths can lead to a stronger, more resilient you.
So, embrace the challenge, mix and match techniques, and listen to your body as you embark on this journey. After all, the true victory lies not in the choice between weightlifting and bodyweight training, but in the commitment to a healthier, more active lifestyle. Happy lifting, and don’t forget to celebrate the small victories along the way!





Leave a Reply